Skin Infections and Traditional Herbal Treatment
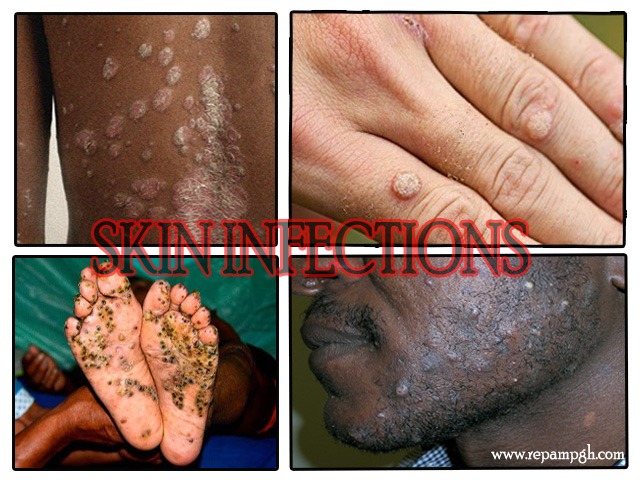
A skin infection occurs when germs, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, penetrate the skin and spread. These infections can cause various symptoms, including pain, swelling, redness, inflammation, or the formation of abscesses. An example is Herpes simplex virus (HSV): Which causes cold sores or genital herpes. The transmission of skin infections can occur in several ways, depending on the type of infection, which can result from animal bites, insect bites, direct contact, sharing objects, environment exposure and breaks in the skin.
The Causes of skin infection
Skin infections can be caused by a variety of factors, often involving different types of microorganisms. Here are the primary causes:
- Bacteria: Bacterial skin infections occur when bacteria like Staphylococcus or Streptococcus enter the skin through a cut, wound, or hair follicle. Conditions such as diabetes, poor circulation, or a weakened immune system can increase the risk of bacterial infections.
- Viruses: Viral skin infections are caused by viruses such as the herpes simplex virus (causing cold sores), human papillomavirus (causing warts), or the varicella-zoster virus (causing chickenpox and shingles).
- Fungi: Fungal skin infections are typically caused by dermatophytes or yeasts, which thrive in warm, moist environments. Common fungal infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections.
- Parasites: Parasitic skin infections are caused by parasites such as lice, scabies mites, or ticks. These organisms live on or in the skin and can cause symptoms like itching and rashes.
Environmental factors, personal hygiene, and lifestyle choices can also contribute to the development of skin infections. For example, frequenting communal showers or locker rooms can increase the risk of fungal infections, while close contact with someone who has a contagious skin infection can lead to transmission
It’s important to maintain good skin care practices, keep wounds clean, and avoid sharing personal items like towels or razors to help prevent skin infections. If you suspect a skin infection, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment
What are the symptoms of skin infections
Causes of skin infections